Projekt LoRaWAN: Unterschied zwischen den Versionen
Aus Opennet
Thm (Diskussion | Beiträge) (→Merkzettel) |
Thm (Diskussion | Beiträge) |
||
| Zeile 37: | Zeile 37: | ||
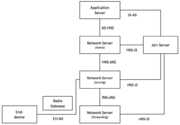
[[Datei:LoRaWAN-NRM.png|mini|LoRaWAN Network Reference Model (NRM), roaming End-Device (aus LoRaWAN Backend Interfaces 1.0 Specification)]] | [[Datei:LoRaWAN-NRM.png|mini|LoRaWAN Network Reference Model (NRM), roaming End-Device (aus LoRaWAN Backend Interfaces 1.0 Specification)]] | ||
| − | = | + | = LoRaWAN bei Opennet = |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
== Nutzen für Opennet == | == Nutzen für Opennet == | ||
| Zeile 72: | Zeile 44: | ||
* Bereitstellen eines Community LoRaWANs in Rostock und ggfs. sonstwo | * Bereitstellen eines Community LoRaWANs in Rostock und ggfs. sonstwo | ||
* Eigene Nutzungsmöglichkeiten | * Eigene Nutzungsmöglichkeiten | ||
| + | ** Anwendungen vor allem Sensordaten erfassen, Fernsteuern, Überwachen [[Datei:esp32lora.jpg|mini|ESP32)]] | ||
| + | ** Gateways ab 100,-EUR ohne Outdoor-Gehäuse und Antennen | ||
| + | ** Eigene Clients zum Basteln je nach Anwendung | ||
== Standorte == | == Standorte == | ||
| Zeile 88: | Zeile 63: | ||
* Standorte so planen, dass gesamte Stadt abgedeckt wird | * Standorte so planen, dass gesamte Stadt abgedeckt wird | ||
| − | == | + | == Ausprobierte Hardware == |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
* Unser erstes Gateway soll so aussehen: https://github.com/ttn-zh/ic880a-gateway/wiki | * Unser erstes Gateway soll so aussehen: https://github.com/ttn-zh/ic880a-gateway/wiki | ||
* Ein iC880A-SPI - LoRaWAN Concentrator 868 MHz bestellt - http://shop.imst.de/wireless-modules/lora-products/8/ic880a-spi-lorawan-concentrator-868-mhz | * Ein iC880A-SPI - LoRaWAN Concentrator 868 MHz bestellt - http://shop.imst.de/wireless-modules/lora-products/8/ic880a-spi-lorawan-concentrator-868-mhz | ||
| + | * https://www.amazon.de/MakerHawk-Entwicklungsbrett-Bluetooth-Doppelkern-0-96inch/dp/B076T28KWG | ||
= Merkzettel = | = Merkzettel = | ||
| + | == Hardware == | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Gateways === | ||
| + | |||
| + | * http://www.dragino.com/products/lora/item/117-lg01-p.html | ||
* Raspberry PI: cheap LoRa gateway https://electronza.com/raspberry-pi-cheap-lora-gateway/ | * Raspberry PI: cheap LoRa gateway https://electronza.com/raspberry-pi-cheap-lora-gateway/ | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Endgeräte === | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Arduino, diverse "Shields" für Ardoino und Co. | ||
| + | ** https://www.amazon.de/s/ref=nb_sb_noss?__mk_de_DE=ÅMÅŽÕÑ&url=search-alias%3Daps&field-keywords=lora+shield&rh=i%3Aaps%2Ck%3Alora+shield | ||
| + | ** http://wiki.dragino.com/index.php?title=Lora_Shield | ||
| + | ** https://stefan.schultheis.at/2018/lora-aprs-gw-raspberry-pi-zero/ | ||
| + | ** https://www.exp-tech.de/search?sSearch=dragino LoRa Starter Kit 868 | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Raspberry | ||
| + | ** https://www.elektormagazine.de/news/lorawan-preiswert-und-einfach-mit-raspberry-pi-und-dragino | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Sonstiges | ||
| + | ** https://www.elektormagazine.de/news/review-einstieg-ins-iot-mit-lora-produkten-von-dragino | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Server-Software == | ||
| + | |||
| + | * https://www.loraserver.io | ||
| + | * https://github.com/TheThingsNetwork/ttn | ||
| + | |||
| + | * App-Server z.B. auch via AWS https://www.hackster.io/naresh-krish/integrating-lorawan-with-aws-iot-services-using-the-rak811-b0127d | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Sonstiges == | ||
| + | |||
* http://de.farnell.com/the-things-network/ttn-un-868/the-things-uno-eu/dp/2675815 | * http://de.farnell.com/the-things-network/ttn-un-868/the-things-uno-eu/dp/2675815 | ||
* http://de.farnell.com/das-einmaleins-des-lorawan | * http://de.farnell.com/das-einmaleins-des-lorawan | ||
* https://www.rs-online.com/designspark/building-a-raspberry-pi-powered-lorawan-gateway | * https://www.rs-online.com/designspark/building-a-raspberry-pi-powered-lorawan-gateway | ||
| − | |||
* https://www.amazon.de/gp/product/B01N8SKD2I/ Pycom LoPy - IoT-Entwicklungsboard mit LoRa, WLAN und BLE | * https://www.amazon.de/gp/product/B01N8SKD2I/ Pycom LoPy - IoT-Entwicklungsboard mit LoRa, WLAN und BLE | ||
| − | |||
* https://www.thethingsnetwork.org/forum/t/big-esp32-sx127x-topic-part-1/10247/33 | * https://www.thethingsnetwork.org/forum/t/big-esp32-sx127x-topic-part-1/10247/33 | ||
* https://www.hackerspace-ffm.de/wiki/index.php?title=LoRaWAN | * https://www.hackerspace-ffm.de/wiki/index.php?title=LoRaWAN | ||
Version vom 1. April 2018, 21:56 Uhr
| Team |
| [[Image:|90px]] Projekt LoRaWAN |
| Treffen: nur bei Bedarf |
| LoRa-WAN |
| Mitglieder: Thomas |
| Kontakt: |
Inhaltsverzeichnis |
Knowledge LoRa / LoRa-WAN
Einsatzmöglichkeiten
- Low Energy, low throughput, high bandwidth, long range Übertragung
- Beispiel Sensordaten
- Über LoRa-WAN auch Anbindung ans Internet, im Idealfall überall, dazu Gateways notwendig
- https://de.wikipedia.org/wiki/The_Things_Network stellt solche Gateways als Community bereit
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=3cIGzwH-NI8
Protokoll
- Layer 1 - Chirp Spread Spectrum
- https://de.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chirp_Spread_Spectrum
- In Europa Frequenzen 433 MHz (ISM-Band Region 1) und 868 MHz (SRD-Band Europa)
- Reichweiten von 2 km (Stadtgebiet) über 15 km (Vororte) bis zu 40 km (ländliche Gebiete)
- Layer 2
- Bi-directional end-devices (Class A): End-devices of Class A allow for biirectional communications whereby each end-device’s uplink transmission is followed by two short downlink receive windows. The transmission slot scheduled by the end-device is based on its own communication needs with a small variation based on a random time basis (ALOHA-type of protocol). This Class A operation is the lowest power end-device system for applications that only require downlink communication from the server shortly after the end-device has sent an uplink transmission. Downlink communications from the server at any other time will have to wait until the next scheduled uplink.
- Bi-directional end-devices with scheduled receive slots (Class B): End-devices of Class B allow for more receive slots. In addition to the Class A random receive windows, Class B devices open extra receive windows at scheduled times. In order for the End-device to open its receive window at the scheduled time, it receives a time synchronized Beacon from the gateway.
- Bi-directional end-devices with maximal receive slots (Class C): End-devices of Class C have nearly continuously open receive windows, only closed when transmitting. Class C end-device will use more power to operate than Class A or Class B but they offer the lowest latency for server to end-device communication.
- Layer 3
- https://www.lora-alliance.org/for-developers
- LoRa-WAN ist eine Möglichkeit, ein Low Power Wide Area Network zu errichten
LoRaWAN bei Opennet
Nutzen für Opennet
- Neues Projekt
- Bereitstellen eines Community LoRaWANs in Rostock und ggfs. sonstwo
- Eigene Nutzungsmöglichkeiten
- Anwendungen vor allem Sensordaten erfassen, Fernsteuern, Überwachen
- Gateways ab 100,-EUR ohne Outdoor-Gehäuse und Antennen
- Eigene Clients zum Basteln je nach Anwendung
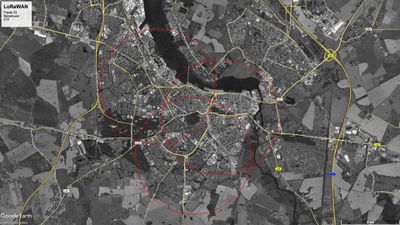
Standorte
Bei 2km Reichweite in Städten würden wir mit den ersten drei Gateways schon die komplette Innenstadt abdecken.
Anbindung
Was wir tun müssten
- Gateways aufstellen
- LoRaWAN Network Server bereitstellen
- Eventuell Anbindung an The Things Network
- Standorte so planen, dass gesamte Stadt abgedeckt wird
Ausprobierte Hardware
- Unser erstes Gateway soll so aussehen: https://github.com/ttn-zh/ic880a-gateway/wiki
- Ein iC880A-SPI - LoRaWAN Concentrator 868 MHz bestellt - http://shop.imst.de/wireless-modules/lora-products/8/ic880a-spi-lorawan-concentrator-868-mhz
- https://www.amazon.de/MakerHawk-Entwicklungsbrett-Bluetooth-Doppelkern-0-96inch/dp/B076T28KWG
Merkzettel
Hardware
Gateways
- http://www.dragino.com/products/lora/item/117-lg01-p.html
- Raspberry PI: cheap LoRa gateway https://electronza.com/raspberry-pi-cheap-lora-gateway/
Endgeräte
- Arduino, diverse "Shields" für Ardoino und Co.
- https://www.amazon.de/s/ref=nb_sb_noss?__mk_de_DE=ÅMÅŽÕÑ&url=search-alias%3Daps&field-keywords=lora+shield&rh=i%3Aaps%2Ck%3Alora+shield
- http://wiki.dragino.com/index.php?title=Lora_Shield
- https://stefan.schultheis.at/2018/lora-aprs-gw-raspberry-pi-zero/
- https://www.exp-tech.de/search?sSearch=dragino LoRa Starter Kit 868
- Raspberry
- Sonstiges
Server-Software
- App-Server z.B. auch via AWS https://www.hackster.io/naresh-krish/integrating-lorawan-with-aws-iot-services-using-the-rak811-b0127d
Sonstiges
- http://de.farnell.com/the-things-network/ttn-un-868/the-things-uno-eu/dp/2675815
- http://de.farnell.com/das-einmaleins-des-lorawan
- https://www.rs-online.com/designspark/building-a-raspberry-pi-powered-lorawan-gateway
- https://www.amazon.de/gp/product/B01N8SKD2I/ Pycom LoPy - IoT-Entwicklungsboard mit LoRa, WLAN und BLE
- https://www.thethingsnetwork.org/forum/t/big-esp32-sx127x-topic-part-1/10247/33
- https://www.hackerspace-ffm.de/wiki/index.php?title=LoRaWAN